Navigating the world of financial trading can be daunting, especially for newcomers. One aspect that often perplexes beginners is the distinction between various brokerage models, such as A-Book and B-Book brokers. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down the fundamentals of B-Book brokers, explaining their operation, importance, scope, advantages, and disadvantages in simple terms for those new to the field of brokerage.
Understanding B-Book Brokers
Definition and Explanation
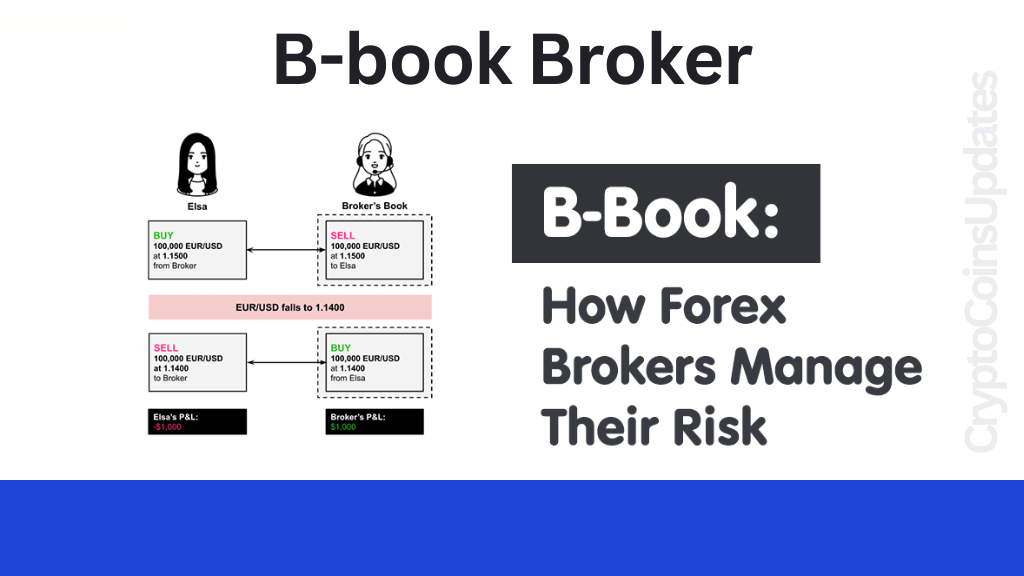
Let’s start with the basics. B-book brokers, also known as Market Makers, differ from traditional A-book brokers in how they handle trades. While A-Book brokers simply pass their clients’ orders onto the market, B-Book brokers internalize trades, essentially becoming the counterparty to their clients’ trades.
How B-Book Brokers Operate
Imagine you place a trade with a B-Book broker. Instead of forwarding your order to the market, the broker executes the trade internally, matching it with another client’s trade or taking the opposite position themselves. This internalization allows for quick trade execution, but it also means the broker profits when their clients lose.
Key Characteristics of B-Book Brokerage Model
B-Book brokers focus on providing instant execution of trades, often offering flexible trading conditions and lower minimum deposit requirements to attract traders. However, this model introduces a conflict of interest, as the broker’s profit is directly tied to their clients’ losses.
Scope of B-Book Brokers
Internalization of Trades
Internalizing trades means B-Book brokers match buy and sell orders from their clients internally, rather than sending them to external markets. While this ensures rapid trade execution, it also raises concerns about transparency and fairness, as the broker profits from clients’ losses.
Profit Mechanisms
B-Book brokers generate revenue through various means, including the spread markup and profits from clients’ losses. This profit model can incentivize brokers to prioritize their own profits over their clients’ success, leading to potential conflicts of interest.
Risk Management Strategies
To mitigate the risk associated with internalizing trades, B-Book brokers employ risk management techniques such as hedging and position management. These strategies aim to balance the broker’s exposure and minimize potential losses, but they can also impact traders’ outcomes.
Regulatory Landscape
Regulatory oversight of B-Book brokers varies across jurisdictions, with some imposing stricter requirements to ensure transparency and protect clients’ interests. Traders should be aware of the regulatory environment when choosing a B-Book broker to ensure adequate protection and recourse in case of disputes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of B-Book Brokers
Advantages
B-Book brokers offer instant execution of trades, allowing traders to enter and exit positions quickly. They also often provide flexible trading conditions and lower minimum deposit requirements, making them accessible to a wide range of traders.
Disadvantages
However, the conflict of interest inherent in the B-Book model raises concerns about fairness and transparency. There’s also the potential for price manipulation, as the broker has control over trade execution and pricing. Additionally, the lack of transparency in how profits are generated can be a cause for concern for traders.
Scope of Services Offered by B-Book Brokers
B-Book brokers typically offer a variety of financial instruments for trading, including currency pairs, commodities, and indices. They also provide user-friendly trading platforms with features and functionalities designed to enhance the trading experience for their clients.
Case Studies and Examples
Real-life examples of B-Book brokers in action illustrate the scope and impact of their brokerage model on traders’ experiences. These case studies highlight both the benefits and pitfalls of trading with B-Book brokers, offering valuable insights for newcomers.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a B-Book Broker
When selecting a B-Book broker, newcomers should consider factors such as their trading objectives, risk tolerance, regulatory compliance, and the broker’s reputation and reliability. Conducting thorough research and due diligence is essential to ensure a positive trading experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of B-Book brokers is essential for newcomers to the field of brokerage. By grasping the basics of how B-Book brokers operate, the scope of their services, and the advantages and disadvantages they offer, newcomers can make informed decisions when choosing a broker that aligns with their trading goals and preferences.
FAQs
- Can B-Book brokers manipulate prices? While B-Book brokers can adjust prices, regulatory oversight and risk management practices aim to minimize the potential for price manipulation.
- How do B-Book brokers make money? B-Book brokers generate revenue through the spread markup and profits from clients’ losses. This profit model can incentivize brokers to prioritize their own profits over their clients’ success.
- Are B-book brokers regulated differently from A-book brokers? Regulatory oversight of B-Book brokers varies, but some jurisdictions impose stricter requirements to ensure transparency and protect clients’ interests.
- What factors should I consider when choosing a B-Book broker? Factors to consider include trading objectives, risk tolerance, regulatory compliance, and the broker’s reputation and reliability. Conducting thorough research and due diligence is essential.
- Are B-Book brokers suitable for beginners? While B-Book brokers offer advantages such as instant execution and flexible trading conditions, newcomers should be aware of the potential conflicts of interest and lack of transparency inherent in this model. It’s essential to choose a broker carefully and consider seeking advice from experienced traders.